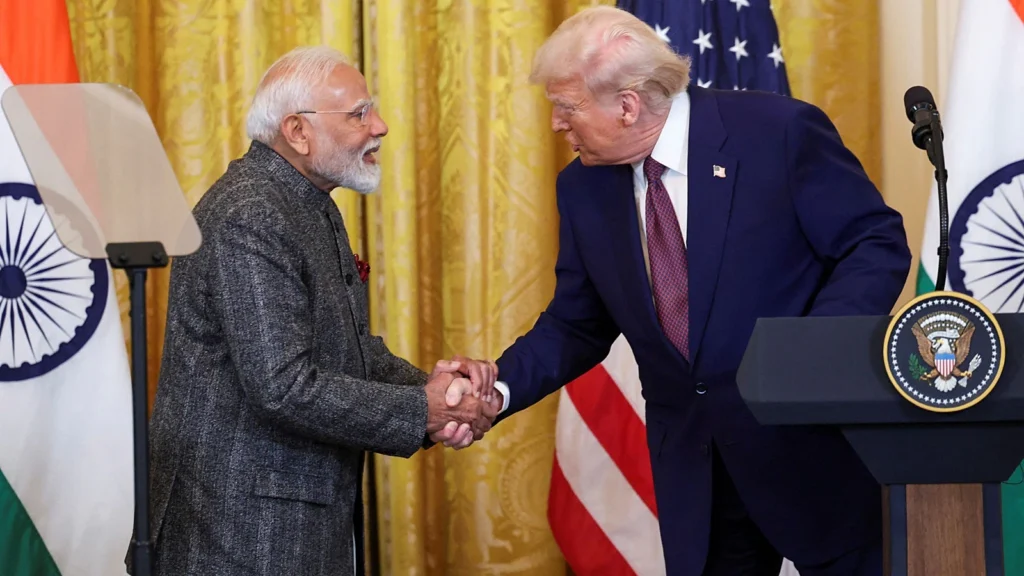
Historic Step Towards Bilateral Trade Agreement
The United States and India have unveiled a new framework for an Interim Trade Agreement, marking a major step toward a comprehensive Bilateral Trade Agreement (BTA). The announcement came after discussions between US President Donald Trump and Prime Minister Narendra Modi, who described the deal as a breakthrough in economic cooperation. Both leaders said the agreement would unlock new opportunities for trade, investment, and strategic partnership between the world’s two largest democracies.
President Trump stated that the US plans to lower tariffs on Indian goods to 18 percent from 25 percent. In return, India has agreed to reduce its dependence on Russian oil. Trump linked the move to global peace efforts, especially regarding the Ukraine conflict. Meanwhile, PM Modi expressed optimism, highlighting that stronger economic ties would benefit people in both nations and enhance global stability.
Major Tariff Reforms and Market Access
According to the White House’s joint statement, India has committed to reducing or removing duties on several US industrial and agricultural products. These include soybean oil, fruits, nuts, animal feed, and alcoholic beverages. The US, on its part, will introduce a reciprocal tariff structure and may remove duties on Indian exports such as gems, aircraft parts, and generic medicines.
Washington also announced plans to roll back certain national-security tariffs on Indian aircraft components and metals. India will receive preferential access in sensitive sectors like automotive parts and pharmaceuticals. Both sides aim to ensure long-term market access in strategically important industries.

Regulatory Cooperation and Trade Safeguards
The agreement places strong emphasis on regulatory alignment and trade safeguards. India and the US will jointly develop rules of origin to prevent third-country misuse of trade benefits. They have also pledged to address long-standing non-tariff barriers, especially in medical devices, ICT imports, and agriculture.
Both countries will work on aligning technical standards and certification processes to make exports easier. A flexibility clause will allow tariff adjustments if either side changes its trade policies in the future. These measures are expected to create a more transparent and predictable trading environment.
Technology, Energy, and Future Cooperation
A key highlight of the framework is enhanced cooperation in economic security and emerging technologies. The two nations will strengthen collaboration in supply chains, export controls, and investment screening. Special focus will be placed on GPUs, data centers, and advanced manufacturing.
India has also expressed its intention to purchase nearly $500 billion worth of US goods over the next five years. These include energy resources, aviation equipment, precious metals, and technology products. Officials believe this commitment will boost American exports while supporting India’s industrial growth.
With this 12-point framework, India and the US have laid a strong foundation for a deeper economic partnership. If implemented effectively, the interim deal could reshape bilateral trade relations and pave the way for a full-scale trade agreement in the near future.